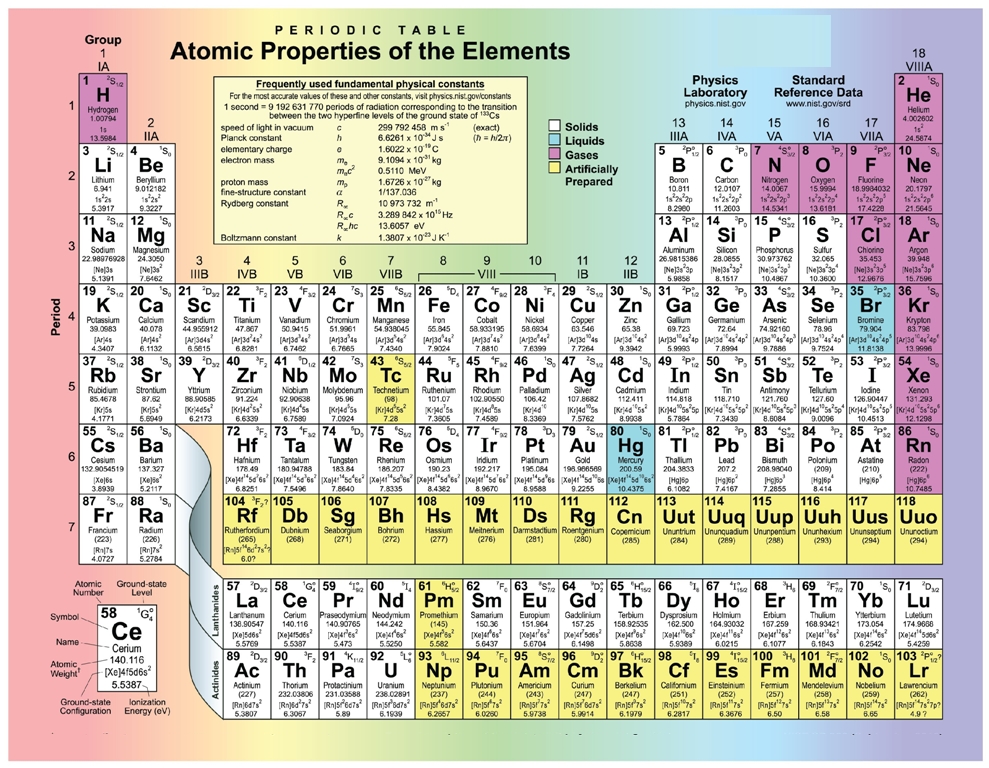
The elements of the periodic table sorted by atomic number
The atomic number. Of an element tells you how many protons that the element has. This is written at the bottom left hand side of the symbol. (only true for the first 20 elements). This is a list of the 118 chemical elements which have been identified as of 2021. A chemical element, often simply called an element, is a species of atoms which all have the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e., the same atomic number, or Z). Study Flashcards On Periodic Table Elements by atomic number (1-20) at Cram.com. Quickly memorize the terms, phrases and much more. Cram.com makes it easy to get the grade you want! Point to the graph to see details, or click for full data on that element.
click on any elements name for further chemical properties, environmental data or health effects.
This list contains the 118 elements of chemistry.
| The chemical elements of the periodic chart sorted by: | Atomic number | Name chemical element | Symbol |
| - Name alphabetically | 1 | Hydrogen | H |
| - Atomic number | 2 | Helium | He |
| - Symbol | 3 | Lithium | Li |
| - Atomic Mass | 4 | Beryllium | Be |
| - Electronegativity | 5 | Boron | B |
| - Density | 6 | Carbon | C |
| - Melting point | 7 | Nitrogen | N |
| - Boiling point | 8 | Oxygen | O |
| - Vanderwaals radius | 9 | Fluorine | F |
| - Year of discovery | 10 | Neon | Ne |
| - Inventor surname | 11 | Sodium | Na |
| - Elements in earthcrust | 12 | Magnesium | Mg |
| - Elements in human body | 13 | Aluminum | Al |
| - Covalenz radius | 14 | Silicon | Si |
| - Ionization energy | 15 | Phosphorus | P |
For chemistry students and teachers: The tabular chart on the right is arranged by Atomic number. The first chemical element is Hydrogen and the last is Ununoctium. Please note that the elements do not show their natural relation towards each other as in the Periodic system. There you can find the metals, semi-conductor(s), non-metal(s), inert noble gas(ses), Halogens, Lanthanoides, Actinoids (rare earth elements) and transition metals. | 16 | Sulfur | S |
| 17 | Chlorine | Cl | |
| 18 | Argon | Ar | |
| 19 | Potassium | K | |
| 20 | Calcium | Ca | |
| 21 | Scandium | Sc | |
| 22 | Titanium | Ti | |
| 23 | Vanadium | V | |
| 24 | Chromium | Cr | |
| 25 | Manganese | Mn | |
| 26 | Iron | Fe | |
| 27 | Cobalt | Co | |
| 28 | Nickel | Ni | |
| 29 | Copper | Cu | |
| 30 | Zinc | Zn | |
| 31 | Gallium | Ga | |
| 32 | Germanium | Ge | |
| 33 | Arsenic | As | |
| 34 | Selenium | Se | |
| 35 | Bromine | Br | |
| 36 | Krypton | Kr | |
| 37 | Rubidium | Rb | |
| 38 | Strontium | Sr | |
| 39 | Yttrium | Y | |
| 40 | Zirconium | Zr | |
| 41 | Niobium | Nb | |
| 42 | Molybdenum | Mo | |
| 43 | Technetium | Tc | |
| 44 | Ruthenium | Ru | |
| 45 | Rhodium | Rh | |
| 46 | Palladium | Pd | |
| 47 | Silver | Ag | |
| 48 | Cadmium | Cd | |
| 49 | Indium | In | |
| 50 | Tin | Sn | |
| 51 | Antimony | Sb | |
| 52 | Tellurium | Te | |
| 53 | Iodine | I | |
| 54 | Xenon | Xe | |
| 55 | Cesium | Cs | |
| 56 | Barium | Ba | |
| 57 | Lanthanum | La | |
| 58 | Cerium | Ce | |
| 59 | Praseodymium | Pr | |
| 60 | Neodymium | Nd | |
| 61 | Promethium | Pm | |
| 62 | Samarium | Sm | |
| 63 | Europium | Eu | |
| 64 | Gadolinium | Gd | |
| 65 | Terbium | Tb | |
| 66 | Dysprosium | Dy | |
| 67 | Holmium | Ho | |
| 68 | Erbium | Er | |
| 69 | Thulium | Tm | |
| 70 | Ytterbium | Yb | |
| 71 | Lutetium | Lu | |
| 72 | Hafnium | Hf | |
| 73 | Tantalum | Ta | |
| 74 | Tungsten | W | |
| 75 | Rhenium | Re | |
| 76 | Osmium | Os | |
| 77 | Iridium | Ir | |
| 78 | Platinum | Pt | |
| 79 | Gold | Au | |
| 80 | Mercury | Hg | |
| 81 | Thallium | Tl | |
| 82 | Lead | Pb | |
| 83 | Bismuth | Bi | |
| 84 | Polonium | Po | |
| 85 | Astatine | At | |
| 86 | Radon | Rn | |
| 87 | Francium | Fr | |
| 88 | Radium | Ra | |
| 89 | Actinium | Ac | |
| 90 | Thorium | Th | |
| 91 | Protactinium | Pa | |
| 92 | Uranium | U | |
| 93 | Neptunium | Np | |
| 94 | Plutonium | Pu | |
| 95 | Americium | Am | |
| 96 | Curium | Cm | |
| 97 | Berkelium | Bk | |
| 98 | Californium | Cf | |
| 99 | Einsteinium | Es | |
| 100 | Fermium | Fm | |
| 101 | Mendelevium | Md | |
| 102 | Nobelium | No | |
| 103 | Lawrencium | Lr | |
| 104 | Rutherfordium | Rf | |
| 105 | Dubnium | Db | |
| 106 | Seaborgium | Sg | |
| 107 | Bohrium | Bh | |
| 108 | Hassium | Hs | |
| 109 | Meitnerium | Mt | |
| 110 | Darmstadtium | Ds | |
| 111 | Roentgenium | Rg | |
| 112 | Copernicium | Cn | |
| 113 | Nihonium | Nh | |
| 114 | Flerovium | Fl | |
| 115 | Moscovium | Mc | |
| 116 | Livermorium | Lv | |
| 117 | Tennessine | Ts | |
| 118 | Oganesson | Og |
First 10 Periodic Table
Click here: for a schematic overview of the periodic table of elements in chart form
Do you need to know the weight of some molecules? Try our Molecular Weight Calculator!
Please report any accidental mistake in the above statistics on chemical elements
Lenntech (European Head Office)
Distributieweg 3
2645 EG Delfgauw
The Netherlands
Phone: +31 152 610 900
fax: +31 152 616 289
e-mail: info@lenntech.com
Lenntech USA LLC (Americas)
5975 Sunset Drive
South Miami, FL 33143
USA
Phone: +1 877 453 8095
e-mail: info@lenntech.com
Lenntech DMCC (Middle East)
Level 5 - OFFICE #8-One JLT Tower
Jumeirah Lake Towers
Dubai - U.A.E.
Phone: +971 4 429 5853
e-mail: info@lenntech.com
Copyright © 1998-2021 Lenntech B.V. All rights reserved
Contents
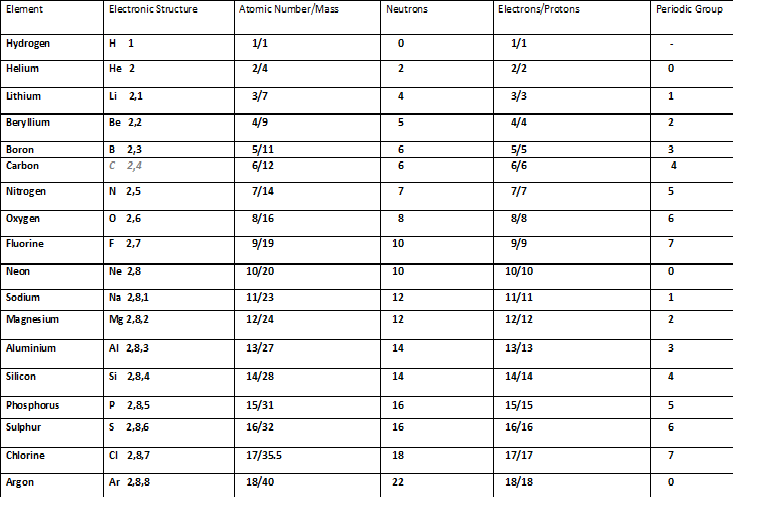
- Atomic number and Mass number
- Isotopes
Atom
An atom is the smallest particle of an element which can take part in chemical reaction. Atom consists of three fundamental particles i.e. proton, neutron and electron. Atoms of same elements are similar in properties whereas atoms of different elements are different in properties. Example:- ‘H’ represent the atom of hydrogen.
Proton is positively charged and electron is negatively charged particle. In an atom, number of protons = number of electrons. Hence, the net charge present in an atom is zero i.e. a free atom is chargeless.
Atomic number and Mass number
Atomic number :
- Atomic number is the number of protons present in an atom.
- The modern periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic number.
Mass number and Atomic mass :
- Mass number is the sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons present in an atom. It is a whole number.
Mass no. of an atom = No. of protons + No. of neutrons
- Atomic mass is the average mass of the all of the isotopes of that element. It is a decimal number.
- For example: Hydrogen has three isotopes – 1H1, 1H2 and 1H3 having mass number 1, 2 and 3 respectively. Naturally occurring hydrogen contains about 99.985% of protium, 0.014% of deuterium and 0.001 % of tritium. Therefore the atomic mass of hydrogen is 1.00784 amu.
- The atomic mass of an element element is measured in atomic mass unit (amu, also known as Daltons ‘ D’or unified atomic mass unit ‘u’).
- 1amu = 1.66 x 10-24 grams. 1gm = 6.022 x 1023 amu ( i.e. Avogadro’s number).
Here,
- Atomic number = Number of protons = Number of electrons = 13
- Mass number = No. of protons + No. of neutrons
- No. of neutrons = Mass number – No. of protons = 27-13 = 14.
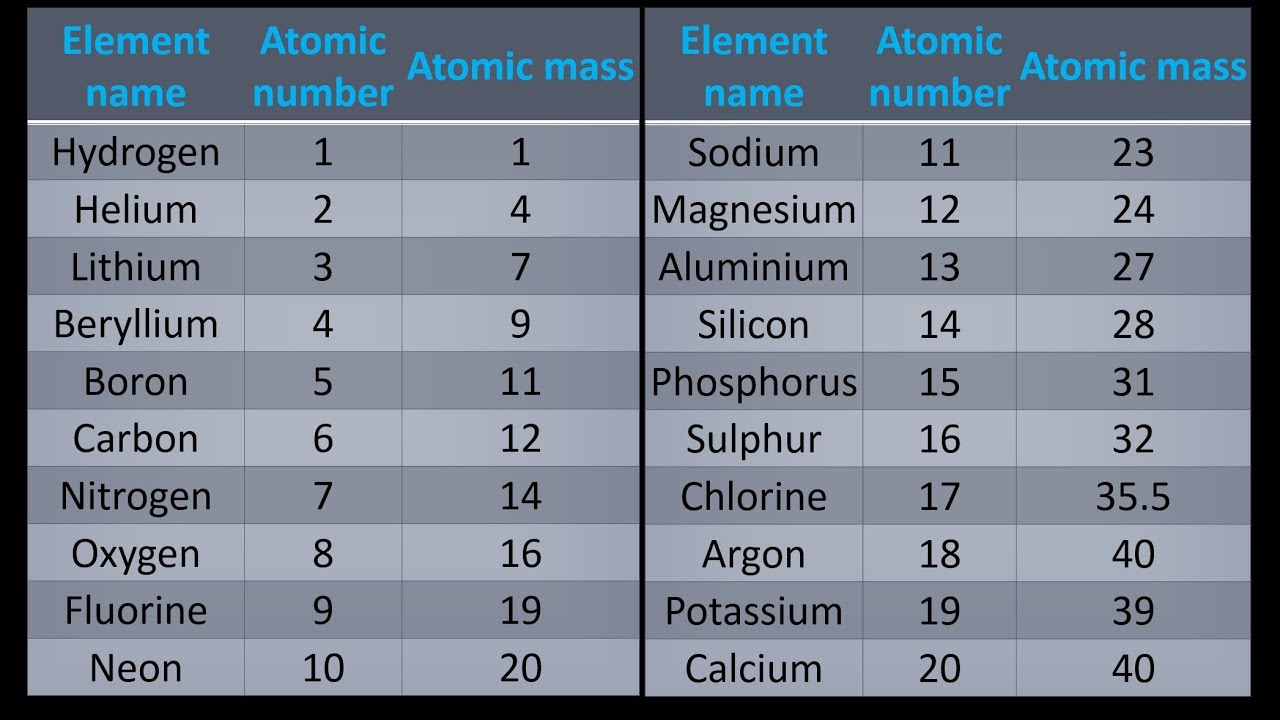
Atomic mass of first 20 elements
| Atomic number | Element | Atomic mass |
| 1 | Hydrogen | 1.008 |
| 2 | Helium | 4.0026 |
| 3 | Lithium | 6.94 |
| 4 | Beryllium | 9.0122 |
| 5 | Boron | 10.81 |
| 6 | Carbon | 12.011 |
| 7 | Nitrogen | 14.007 |
| 8 | Oxygen | 15.999 |
| 9 | Fluorine | 18.998 |
| 10 | Neon | 20.180 |
| 11 | Sodium | 22.990 |
| 12 | Magnesium | 24.305 |
| 13 | Aluminium | 26.982 |
| 14 | Silicon | 28.085 |
| 15 | Phosphorus | 30.974 |
| 16 | Sulfur | 32.06 |
| 17 | Chlorine | 35.45 |
| 18 | Argon | 39.948 |
| 19 | Potassium | 39.098 |
| 20 | Calcium | 40.078 |
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element having same atomic number but different mass number (atomic mass/weight) are called isotopes. For example:
Isotopes of hydrogen :
There are three isotopes of hydrogen:
- Protium or ordinary hydrogen
- Deuterium or heavy hydrogen
- Tritium or radioactive hydrogen.
| Name | Protium | Deuterium | Tritium |
| Symbol | 1H or H | 2H or D | 3H or T |
| No. of protons(P) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| No. of neutrons(n) | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| No. of electrons(e) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Atomic no.(Z) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Mass no.(A) | 1 | 2 | 3 |
Naturally occurring hydrogen contains about 99.985% of protium, 0.014% of deuterium and 0.001 % of tritium.
Isotopes have different physical properties since they differ in their mass number.
They have same chemical properties since their electronic configuration is same. However, they differ in the rate of chemical reaction. For example, D2 reacts with Cl2 about 13 times slower than H2 does. The different in rate of reaction due to difference in mass of the atoms of the same element is called isotope effect.
Some other examples of isotopic elements :
| Elements | Isotopes | Most abundant isotope |
| Carbon | 6C12, 6C13, 6C14 | 6C12 |
| Nitrogen | 7N14, 7N15 | 7N14 |
| Oxygen | 8O16, 8O17, 8O18 | 8O16 |
| Sulphur | 16S32, 16S33, 16S34, 16S36 | 16S32 |
| Chlorine | 17Cl35, 17S37 | 17Cl35 |
Isobars
Atoms of different elements having different atomic number but same mass number are called isobars. For example :
18Ar40, 19K40 and 20Ca40
Isotones
Atoms of different elements having different atomic number and mass number but same number of neutrons are called isotones. For example :
6C14, 7N15 and 8O16
Objective questions and their answers
1. Which of the following is known as heavy hydrogen?
a. Protium c. Tritium
b. Deuterium d. Para hydrogen
2. Which of the following is known as radioactive hydrogen?
a. Protium c. Tritium
b. Deuterium d. Para hydrogen
3. Least abundant isotope of hydrogen is:
a. Protium c. Tritium
b. Deuterium d. Heavy hydrogen
4. Diamond and graphite are :
a. Isotopes c. Isotones
b. Isobars d. Allotropes
5. 6C14 and 8O16 are :
a. Isotopes c. Isotones
b. Isobars d. Allotropes
6. 6C14 and 7N14 are :
a. Isotopes c. Isotones
b. Isobars d. Allotropes
7. All particles residing inside the nucleus of an atom are termed as:
a. Protons c. Electrons
b. Neutrons d. Nucleons
8. What makes the atomic mass fractional ?
a.Prerence of isotopes
b. Number of unpaired electrons
c. Spherical shape
d. Quantum number.
9. Which of the following are not isotopes:
a. 1H1 and 1H3
b. 18K40 and 20Ca40
c. 6C14 and 7N14
d. Both b and c.
10. Charge present in the nucleus of an atom is :
Atomic Number For Elements
a. Positive c. Chargeless
b. Negative d. Both +Ve and -Ve
11. Molecular weight of heavy water is :
a. 16 c. 20
b. 18 d. 22
Answers :
1. b 2. c 3. c
1 To 20 Atomic Number Element
4. d [Note : different forms of same element having different properties are called allotropes]
5. c 6. b 7. d
8. a 9. d 10. a
11. c Note :Heavy water– Deuterium oxide (D2O) is called heavy water. It’s molecular weight is 20 and boiling paint is 101.50C and melting point is 3.80C.
References
- Sthapit, M.K., Pradhananga, R.R., Foundations of Chemistry, Vol 1 and 2, Fourth edition, Taleju Prakashan, 2005.
